
Learn the fingering to use with instruments
Look at fingering changes to learn the basic finger positions to use with instruments.
You can also download fingering charts.
We tried making sounds with materials close at hand. What kind of sounds do these materials make? Please try it for yourself!

In this experiment, a reed is made using a juice straw, and the sound is compared to that produced by an ordinary reed.

Try rolling up a transparent sheet in various ways and attaching a clarinet mouthpiece. What sounds does this produce?

As was stated previously, changing the taper (the degree of graduation) changes the timbre and pitch of the instrument, but in what way? We used a mouthpiece and paper to find out.

As was stated previously, changing the taper (the degree of graduation) changes the timbre and pitch of the instrument,in the next experiment, we changed the length of the tube.

Does the sound change according to whether the bore of a tone hole is cut obliquely or straight? We performed an experiment with a vinyl chloride tube.

It is said that the timbre of the bassoon depends on the thickness of the wood surrounding the bore. Let's listen to the timbres of sound produced by an exposed bore, as well as bored enclosed in different materials.

Inserting natural cork in the head joint affects the sound quality. What will happen, however, if we insert another substance instead of cork?
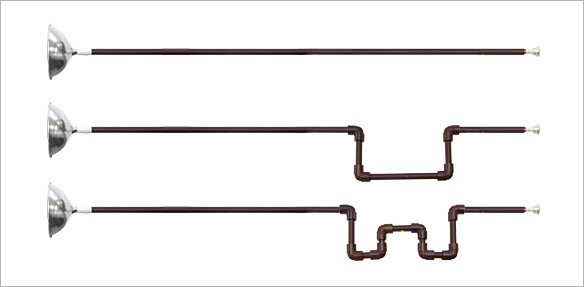
Pressing the trumpet's valves increases the length of the path of the sound, making the note lower overall. Try out this mechanism using a vinyl tube.

If you straightened the entire tubing of a typical tenor trombone, it would end up being 270 cm from mouthpiece to the end of the bell.

The position and shape of the hand inside the bell influences the pitch and timbre, so we experimented with placing objects of differing shapes inside the bell.

What effect does the size of the sound hole have on the sound? We compared the sound as we changed the size of the hole.

The top plays an extremely important role in body resonance. If we change the material of the top what will happen? We tried using a variety of materials.

The strings on a guitar are supported by the saddle and nut. Although these parts were once made from ivory, they are now made from materials such as animal bones, hardened plastic, or brass. What would happen if we replaced these parts with paper or rubber?

It was mentioned earlier that the number of times a coil is wound and even how it is wound (pitch, etc.) can have a significant effect on the timbre and volume. A coil does not need to be wound thousands of time for this change to be noticeable-even 200 times is enough. Let's give it a try.

The design of the body is extremely important for classical guitars to produce a beautiful sounding timbre. Let's change the thickness of the wood used for the body to see how this changes the sound of the guitar.

The bridge is usually made from maple, but this experiment used bridges made with different materials.

We used a variety of materials as bow hair instead of horsehair.

How does the sound change when other materials are substituted for the felt part of the hammer? We experimented with various materials to make the hammer.

If you take a look inside the piano, you can see holes in the metallic frame. What effect does it have on the sound if these holes are blocked? We made cardboard covers and tested the sound produced when these covers were in place.

Some professional drummers put objects inside their bass drums to change the tone. Thus, we conducted an experiment to see how different items inserted into a bass drum changed its tone.

Sometimes a hole is created in the head to change the tone of a drum. So, we made several different holes in the bottom head of a tom-tom and compared their tones.

What happens to the tone of the snare drum when different materials are used for the snare? We used different materials for the snare and conducted an experiment.

When the central portion of the underside of the tone plate is sanded down, the note it produces is lowered. How much does the note go down for a given amount sanded off? Try sanding down a little bit at a time.

Sanding down the central portion of the underside of the tone plate makes the note lower. What would happen if the ends were sanded down, instead? Try it and see.

The material used to make resonator pipes is metal. How might the sound change if a different material were used, instead? We tried experimenting with various materials.